GAUSS’S LAW
The surface integral of
electrostatic field E produce by any source over any closed surface S enclosing a
volume V in vacuum i.e. total electric flux over the closed surface S in vacuum
is 1/epsilon times the total charge Q contained inside S.
The surface chosen to
calculate the surface integral is called Gaussian
surface.
PROOF OF GAUSSIAN
THEOREM
The flux through area element ΔS is
The unit vector rˆ is along the radius vector from the centre to
the area element. Now, since the normal to a sphere at every point is along the
radius vector at that point, the area element ΔS and rˆ have the same
direction. Therefore,
SIGNIFICANCE
OF GAUSS’S LAW
(i)
Gauss’s law is true for any
closed surface, no matter what its shape or size.
(ii)
The term q on the right side
of Gauss’s law includes the sum of all charges enclosed by the surface. The
charges may be located anywhere inside the surface.
(iii)
In the situation when the
surface is so chosen that there are some charges inside and some outside, the
electric field is due to all the charges, both inside and outside S. The term q
on the right side of Gauss’s law.
(iv)
Gauss’s law is often useful
towards a much easier calculation of the electrostatic field when the system
has some symmetry. This is facilitated by the choice of a suitable Gaussian
surface.
(v)
Finally, Gauss’s law is based
on the inverse square dependence on distance contained in the Coulomb’s law.
Any violation of Gauss’s law will indicate departure from the inverse square
law.


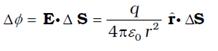



Good
ReplyDeleteGood
DeleteGreat notes! Thanks!
ReplyDeleteGood evening Sir Me atul Rawat hun Ghaziabad wala
ReplyDeleteaapke hi notes chiye the mujhe jo yaha pe mil gaye. Thanks a Lot.
Good notes guys!!!
ReplyDeleteThank you so much ��
ReplyDeletenot to good....
ReplyDeleteyaar itni achchhi explanation hai or kya chhahiye
DeleteProve is using surface as sphere(Special Case). General Proof-http://web.mit.edu/viz/EM/visualizations/coursenotes/modules/guide04.pdf
ReplyDeletegood n ty
ReplyDeletegood n ty
ReplyDeletethanks ....
ReplyDeleteGood but it is of NCERT book
ReplyDeletenice notes
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeletewhy flux through a closed surface containing charge q is equal to q by E0 for any surface??
ReplyDeletehaaa
ReplyDeleteNice
ReplyDeleteThanks sir your best notes
ReplyDeleteThanks sir your best notes
ReplyDeleteSimply superb... Thanks a lot Sir
ReplyDeleteTijy
DeleteShow by using the suitable example that gauss theorem is based on Coulomb's Inverse Square Law
ReplyDeleteNice notes sir. ....Proved very helpful
ReplyDeleteHelpful notes air
ReplyDelete